verl 框架:3. 加载数据与创建 batch
verl 框架:3. 加载数据与创建 batch
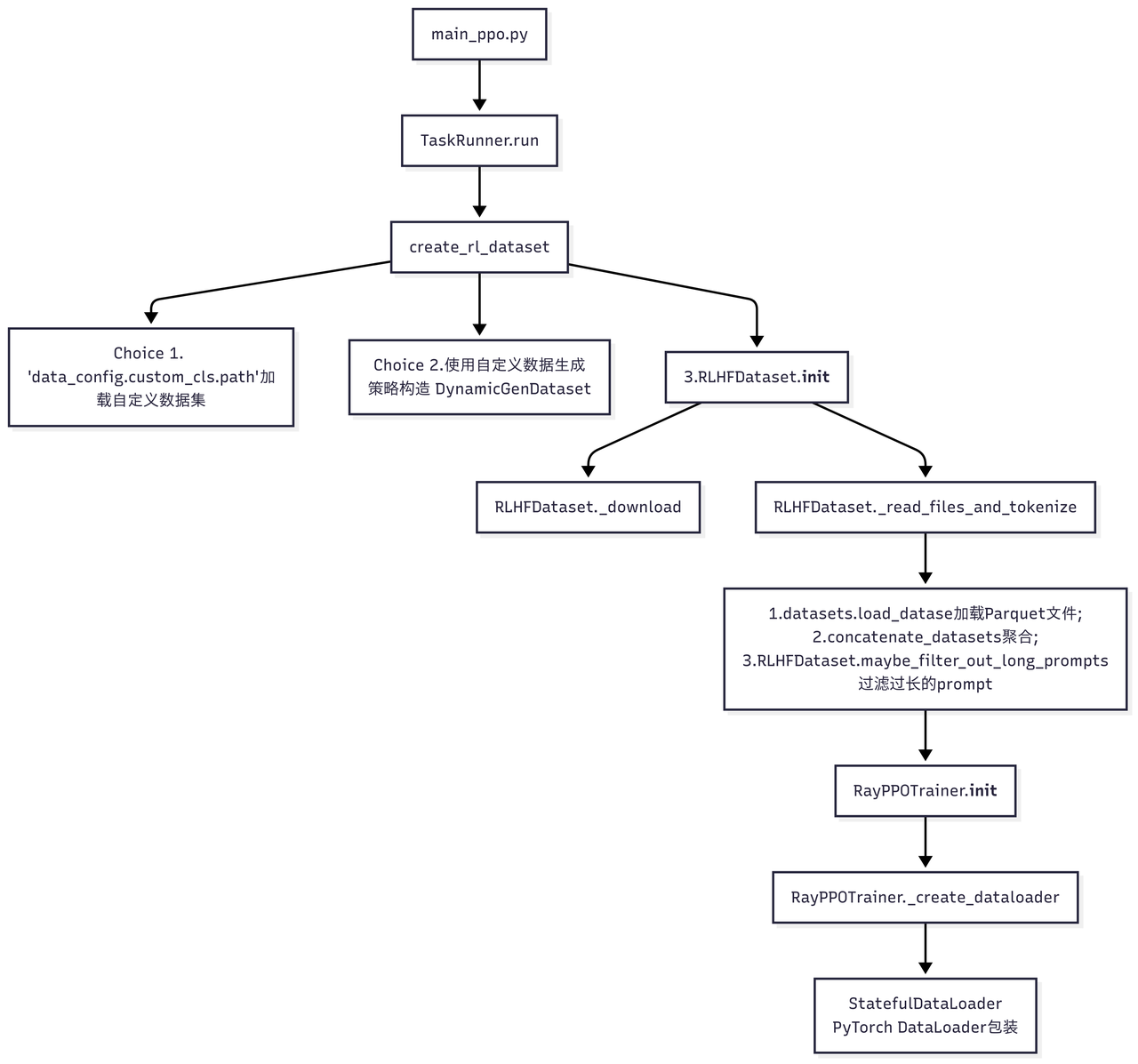
run_ppo()函数完成 Ray 集群初始化之后,创建一个TaskRunner将整个 RL 训练流程封装在一个独立的 Ray Actor 中,提交到远程执行,以支持分布式调度。
TaskRunner.run运行在远程 Ray Actor 中,流程如下(重点关注 PPO 训练器RayPPOTrainer中的 dataset 来源):
1 | def run(self, config): |
创建 RLHFDataset
RayPPOTrainer传入的train_dataset, val_dataset通过调用create_rl_dataset生成:
1 | def create_rl_dataset(data_paths, data_config, tokenizer, processor, is_train=True): |
创建了一个RLHFDataset实例,具体实现如下:
1 | class RLHFDataset(Dataset): |
包含以下功能:
- 支持从远程存储下载 Parquet 文件到本地缓存,支持共享内存加速文件访问;
- 支持多进程并行过滤过长的 prompts(通过
doc2len可配置过滤策略); - 支持纯文本、图像和视频的多模态输入,解析
<image>和<video>标签,将多模态内容转换为结构化格式; - 添加 chat template 格式化对话,将文本转换为 token IDs,生成 attn mask 和 position ids;
- padding 到指定长度,支持多种截断策略(left, right, middle, error),生成位置编码。
第3, 4, 5条是何时实现的呢?遍历单个样本调用RLHFDataset.__getitem__() 时:
1 | def __getitem__(self, item): |
对比 row_dict 在 RLHFDataset.__getitem__() 处理前后的差异:
输入:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13row_dict = {
"data_source": "hiyouga/geometry3k",
"prompt": [{"role": "user", "content": "问题内容"}],
"images": [图像数据],
"ability": "math",
"reward_model": {"style": "rule", "ground_truth": "答案"},
"extra_info": {
"split": "train",
"index": 0,
"answer": "答案",
"question": "问题",
}
}输出:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25row_dict = {
# 原始字段
"data_source": "hiyouga/geometry3k",
"ability": "math",
"reward_model": {"style": "rule", "ground_truth": "答案"},
"extra_info": {...},
# 新增的 tensor 字段
"input_ids": torch.Tensor, # shape: [seq_len]
"attention_mask": torch.Tensor, # shape: [seq_len]
"position_ids": torch.Tensor, # shape: 纯文本模型[seq_len]; 多模态模型[4, seq_len] (Qwen2VL/GLM4V)
"raw_prompt_ids": List[int], # 原始 prompt 的 token IDs
# 多模态字段(如果有)
"multi_modal_data": {
"image": [处理后的图像数据],
"video": [处理后的视频数据]
},
"multi_modal_inputs": {...}, # 多模态输入
# 其他字段
"index": int, # 样本索引
"tools_kwargs": dict, # 工具参数
"interaction_kwargs": dict, # 交互参数
}
输出包含长度均为 [seq_len] 的 input_ids, attention_mask, position_ids(针对纯文本,多模态时格式不同), raw_prompt_ids的 Tensor 字段。
pad 和 truncate 在针对 input ids 和 attn mask 的后处理计算postprocess_data函数中完成,这里引入的是 verl.utils.torch_functional 中相关函数(通过 import ... as verl_F 引入),用以处理 tokenizer 的输出,并 pad/truncate 到恒定长度。
1 | def postprocess_data( |
注意
RLHFDataset.__getitem__()中位置编码的计算:提供了标准文本模型、QWen2VL、GLM4 的模型的位置编码(后两者在verl/model/transformer)中提供。
- 标准文本模型:通过
compute_position_id_with_mask函数基于 attn mask 计算位置编码:只对有效 token 分配连续的位置 ID;填充位置的位置 ID 为 0
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
return torch.clip(torch.cumsum(mask, dim=-1) - 1, min=0, max=None)
# 单样本示例:
# 输入掩码:前4个是有效token,后3个是填充
mask = torch.tensor([1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0])
# 步骤1:累积求和
cumsum_result = torch.cumsum(mask, dim=-1)
print("累积求和:", cumsum_result)
# 输出: tensor([1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4])
# 步骤2:减1
minus_one = cumsum_result - 1
print("减1后:", minus_one)
# 输出: tensor([0, 1, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3])
# 步骤3:裁剪
position_ids = torch.clip(minus_one, min=0, max=None)
print("最终位置编码:", position_ids)
# 输出: tensor([0, 1, 2, 3, 0, 0, 0])
- QWen2VL 使用 3D RoPE 位置编码实现多模态数据的统一处理。官方实现:https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/v4.52.4/src/transformers/models/qwen2_5_vl/modeling_qwen2_5_vl.py#L1405
官方支持批量导入,同时返回位置编码和增量;输出为:
position_ids: (3, batch_size, sequence_length) - 3D 位置编码mrope_position_deltas: (batch_size, 1) - 位置编码增量:计算位置编码的最大值与实际序列长度的差值,用于后续的位置编码调整。
打包为 batch
RayPPOTrainer传入的 collate_fn 通过from verl.utils.dataset.rl_dataset import collate_fn引入,该函数的作用是将若干数据聚集成一个 batch。
1 | # verl/utils/dataset/rl_dataset.py |
对比collate_fn打包前后的输入和输出:
输入:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40# 单个样本示例
sample = {
# === 张量字段 (torch.Tensor) ===
"input_ids": torch.tensor([1, 2, 3, 0, 0]), # shape: (seq_len,)
"attention_mask": torch.tensor([1, 1, 1, 0, 0]), # shape: (seq_len,)
"position_ids": torch.tensor([0, 1, 2, 0, 0]), # shape: (seq_len,) 或 (4, seq_len) 多模态
"raw_prompt_ids": [1, 2, 3], # List[int]
# === 多模态字段 (可选) ===
"multi_modal_data": { # dict
"image": [processed_image_tensor], # List[torch.Tensor]
"video": [processed_video_tensor] # List[torch.Tensor]
},
"multi_modal_inputs": { # dict (可选)
"image_grid_thw": torch.tensor([[1, 2, 2]]), # shape: (1, 3)
"video_grid_thw": torch.tensor([[2, 2, 2]]), # shape: (1, 3)
"second_per_grid_ts": torch.tensor([1.0]) # shape: (1,)
},
# === 非张量字段 (各种类型) ===
"data_source": "hiyouga/geometry3k", # str
"ability": "math", # str
"reward_model": { # dict
"style": "rule",
"ground_truth": "42"
},
"extra_info": { # dict
"split": "train",
"index": 0,
"answer": "42",
"question": "What is 6*7?"
},
"index": 0, # int
"tools_kwargs": {}, # dict
"interaction_kwargs": {}, # dict
# === 可选字段 ===
"raw_prompt": [{"role": "user", "content": "..."}], # List[dict] (可选)
"full_prompts": "<|im_start|>user\n...", # str (可选)
}输出:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47batch_dict = {
# === 张量字段 ===
"input_ids": torch.tensor([
[1, 2, 3, 0, 0], # 样本1
[4, 5, 6, 7, 0] # 样本2
]), # shape: (batch_size, seq_len)
"attention_mask": torch.tensor([
[1, 1, 1, 0, 0], # 样本1
[1, 1, 1, 1, 0] # 样本2
]), # shape: (batch_size, seq_len)
"position_ids": torch.tensor([
[0, 1, 2, 0, 0], # 样本1
[0, 1, 2, 3, 0] # 样本2
]), # shape: (batch_size, seq_len)
# === 非张量字段 ===
"raw_prompt_ids": np.array([
[1, 2, 3], # 样本1
[4, 5, 6, 7] # 样本2
], dtype=object), # shape: (batch_size,)
"data_source": np.array([
"geo3k", # 样本1
"geo3k" # 样本2
], dtype=object), # shape: (batch_size,)
"ability": np.array([
"math", # 样本1
"math" # 样本2
], dtype=object), # shape: (batch_size,)
"reward_model": np.array([
{"style": "rule", "ground_truth": "42"}, # 样本1
{"style": "rule", "ground_truth": "56"} # 样本2
], dtype=object), # shape: (batch_size,)
"extra_info": np.array([
{"split": "train", "index": 0}, # 样本1
{"split": "train", "index": 1} # 样本2
], dtype=object), # shape: (batch_size,)
"index": np.array([0, 1], dtype=object), # shape: (batch_size,)
"tools_kwargs": np.array([{}, {}], dtype=object), # shape: (batch_size,)
"interaction_kwargs": np.array([{}, {}], dtype=object) # shape: (batch_size,)
}
RayPPOTrainer.fit()
回到RayPPOTrainer.fit().
初始化:
- 创建 Tracking 日志记录器:使用 Tracking 类初始化,配置项目名、实验名、日志后端(如 wandb、tensorboard),将完整配置(
OmegaConf.to_container)记录到日志系统; - 初始化全局步数:
self.global_steps = 0; - 加载检查点以恢复模型状态、优化器状态和训练进度;
- 训练前验证(可选);
- 设置 Rollout Skip(可选):如果
skip_rollout=True,使用RolloutSkip包装generate_sequences,跳过实际生成; - 使用 tqdm 创建进度条,显示训练进度,并设置初始步数;
- 初始化性能分析状态;
主训练外层循环(Epoch 迭代)+内层循环(Batch 迭代):
1 | for epoch in range(self.config.trainer.total_epochs): |
对于内层循环中的每个 batch:
调用
_start_profiling()启动所有WorkerGroup的性能分析;准备数据:将
batch_dict转换为DataProto,同时为每个样本生成唯一的 UUID;提取用于 rollout 的数据(移除
input_ids,attention_mask,position_ids等;只保留data_source,reward_model,extra_info,uid等字段);根据
async_rollout_mode选择同步/异步的 rollout 方式并生成序列,记录生成时间;处理 REMAX 基线(可选):生成确定性基线序列,计算基线奖励,用于 REMAX 优势估计器;
为每个样本分配唯一 ID,重复数据以对齐多次采样,计算响应掩码
response_mask(用于区分实际生成部分和 padding),并可选地进行批次平衡;batch 平衡(可选):重新排序数据使每个 dp rank 的总 token 数均衡(不影响基于 uid 的 advantage 计算,可能影响 mini-batch 的 loss 计算);
根据配置使用奖励模型或自定义奖励函数计算 token 级别的奖励分数,支持同步和异步计算;
使用 megatron 基于训练开始前的 policy 重新计算 behaviour policy 的 log probabilities,用于重要性采样,同时计算熵值;
使用 reference policy 计算 log probs,用于 KL 散度计算;
使用 Critic 网络计算状态价值,用于优势函数估计;
根据配置的优势估计器(GAE、GRPO、REMAX 等)计算优势函数,支持 KL 惩罚;
使用计算出的优势函数更新 Critic 网络参数;
在 Critic 预热完成后,使用 PPO 损失函数更新 Actor 网络参数;
将生成的序列、输入、输出和分数保存到指定目录;
根据配置的频率执行验证,计算验证指标并记录;
根据配置的频率保存模型检查点;
收集训练指标、时序指标和吞吐量指标,并记录到日志系统;
更新进度条,递增全局步数,并在达到总训练步数时结束训练;
根据配置在特定步数启用/禁用性能分析,用于调试和优化。
使用 tqdm 创建进度条,显示训练进度,并设置初始步数;
遍历配置的 total_epochs 数和 train_dataloader,每个 train_batch 完成多步更新;
从 batch 中分离出不用于 rollout 的数据(input_ids, attention_mask, position_ids 等),保留其他数据用于后续处理;
1 | def fit(self): |
创建 DataLoader:
RayPPOTrainer.create_dataloaderself.train_dataloader的来源是什么呢?由RayPPOTrainer._init_调用RayPPOTrainer._create_dataloader创建:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
class RayPPOTrainer:
def __init__(
......
collate_fn=None, # 将 data samples 聚合为 batch
train_sampler: Optional[Sampler] = None,
):
self.train_dataloader = StatefulDataLoader(
dataset=self.train_dataset, # RLHFDataset 实例
batch_size=self.config.data.get("gen_batch_size", self.config.data.train_batch_size),
num_workers=num_workers, # 并行加载进程数
drop_last=True, # 丢弃最后一个不完整的 batch
collate_fn=collate_fn, # 批处理函数
sampler=train_sampler, # 采样器
)
RayPPOTrainer.fit()的训练循环中:for batch_dict in self.train_dataloader
2
3
for epoch in range(self.config.trainer.total_epochs):
for batch_dict in self.train_dataloader:以上
batch_dict来自哪儿呢?
RayPPOTrainer.__init__->RayPPOTrainer._create_dataloader->StatefulDataLoader.__iter__() -> DataLoader.__iter__()(Pytorch) -> 遍历数据集for i in range(len(dataset)):-> 获取单个样本dataset[i] -> RLHFDataset.__getitem__(i)-> 打包成 batchcollate_fn([sample1, sample2, ..., sampleN])得到原始的 batch:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
# === 张量字段 ===
"input_ids": torch.tensor([
[1, 2, 3, 0, 0], # 样本1
[4, 5, 6, 7, 0] # 样本2
]), # shape: (batch_size, seq_len)
"attention_mask": torch.tensor([
[1, 1, 1, 0, 0], # 样本1
[1, 1, 1, 1, 0] # 样本2
]), # shape: (batch_size, seq_len)
"position_ids": torch.tensor([
[0, 1, 2, 0, 0], # 样本1
[0, 1, 2, 3, 0] # 样本2
]), # shape: (batch_size, seq_len)
# === 非张量字段 ===
......
"data_source": np.array([
"geo3k", # 样本1
"geo3k" # 样本2
], dtype=object), # shape: (batch_size,)
"reward_model": np.array([
{"style": "rule", "ground_truth": "42"}, # 样本1
{"style": "rule", "ground_truth": "56"} # 样本2
], dtype=object), # shape: (batch_size,)
"extra_info": np.array([
{"split": "train", "index": 0}, # 样本1
{"split": "train", "index": 1} # 样本2
], dtype=object), # shape: (batch_size,)
}
DataFlow
RayPPOTrainer.fit()的数据流具体如下:
parquet 文件
1
data_files = "~/data/rlhf/gsm8k/train.parquet"
RLHFDataset
1
2
3
4
5
6dataset = RLHFDataset(
data_files=data_paths,
tokenizer=tokenizer,
processor=processor,
config=data_config,
)DataLoader
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8self.train_dataloader = StatefulDataLoader(
dataset=self.train_dataset, # RLHFDataset 实例
batch_size=self.config.data.get("gen_batch_size", self.config.data.train_batch_size),
num_workers=num_workers, # 并行加载进程数
drop_last=True, # 丢弃最后一个不完整的 batch
collate_fn=collate_fn, # 批处理函数
sampler=train_sampler, # 采样器
)DataProto
1
2
3for batch_dict in self.train_dataloader:
......
batch: DataProto = DataProto.from_single_dict(batch_dict)pop 提取用于 rollout 的数据:
1
gen_batch = self._get_gen_batch(batch)
通过 rollout 生成序列:
1
2
3
4gen_batch_output = gen_batch.repeat(
repeat_times=self.config.actor_rollout_ref.rollout.n, interleave=True
)
gen_batch_output = self.actor_rollout_wg.generate_sequences(gen_batch_output)将生成的数据
gen_batch合并到 batch:1
batch = batch.union(gen_batch_output)
计算 reward:
1
2reward_tensor, reward_extra_infos_dict = compute_reward(batch, self.reward_fn)
batch.batch["token_level_scores"] = reward_tensor计算 advantage:
1
2
3
4
5batch = compute_advantage(
batch,
adv_estimator=self.config.algorithm.adv_estimator,
......
)重新计算
log_probs:1
2old_log_prob = self.actor_rollout_wg.compute_log_prob(batch)
batch = batch.union(old_log_prob)计算 reference model 的 log_probs:
1
2
3if self.use_reference_policy:
ref_log_prob = self.ref_policy_wg.compute_ref_log_prob(batch)
batch = batch.union(ref_log_prob)计算 value function:
1
2
3if self.use_critic:
values = self.critic_wg.compute_values(batch)
batch = batch.union(values)更新 critic:
1
2
3
4if self.use_critic:
critic_output = self.critic_wg.update_critic(batch)
critic_output_metrics = reduce_metrics(critic_output.meta_info["metrics"])
metrics.update(critic_output_metrics)更新 actor:
1
actor_output = self.actor_rollout_wg.update_actor(batch)
返回训练指标:
1
2
3actor_output_metrics = reduce_metrics(actor_output.meta_info["metrics"])
metrics.update(actor_output_metrics)
logger.log(data=metrics, step=self.global_steps)
除了最初的三步,后续步骤均通过 DataProto 完成数据交换。